Industrial ceramic materials are made up of non-metallic, inorganic chemicals. Products created from industrial ceramics have a high alumina content. These compounds differ greatly from ceramics used for recreational and art purposes. While all ceramics posses certain advantageous characteristics, ceramics suited to industry must be highly resistant to a variety of elements. Read More…
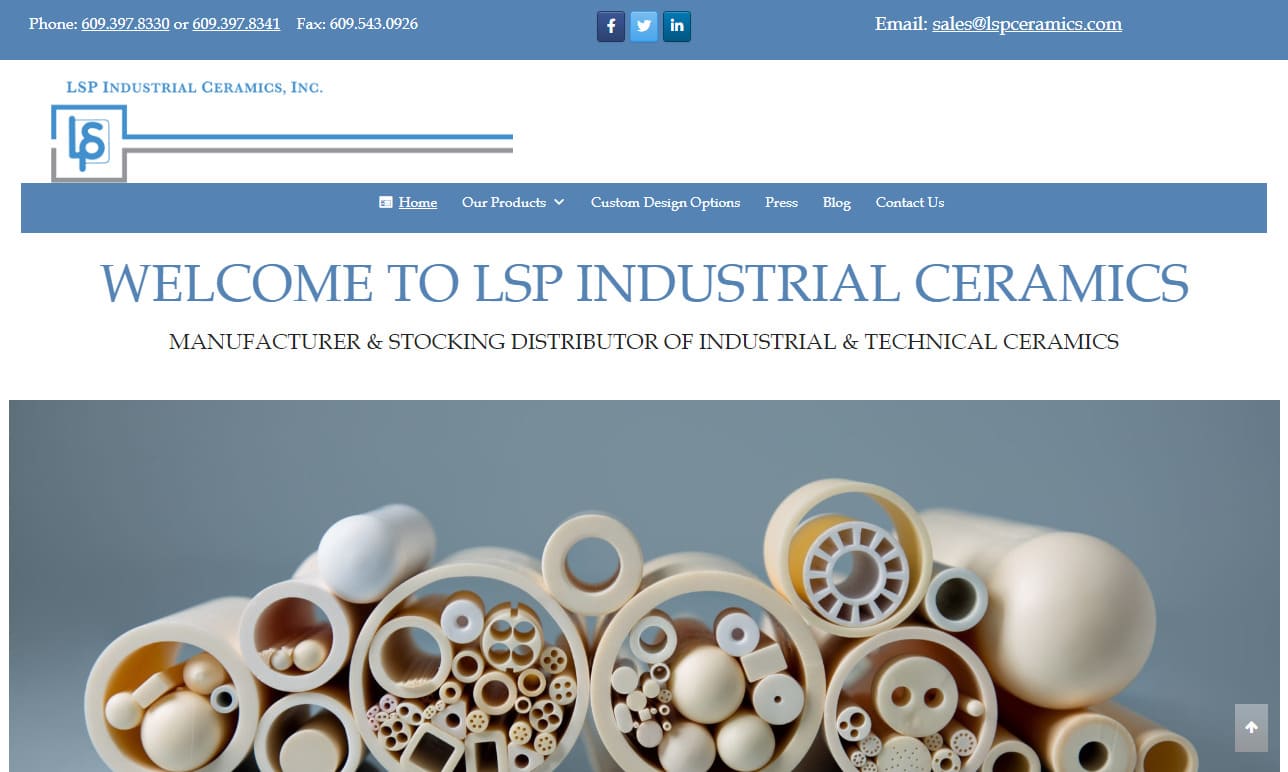
As a manufacturer and stocking distributor of industrial and technical ceramics, LSP carries the most diversified inventory of ceramic tubes, spacers, bushings, etc. in the industry.
C-Mac International manufactures custom advanced technical ceramic solutions. Our specialties are Zirconia (MgO stabilized and Yttria stabilized), Alumina (90%, 96%, and 99.5% purity), and Tungsten Carbide (Cobalt and Nickel Binder). We also work with steatite, cordierite, silicon nitride, ceramic crucibles, and crushable ceramics. We prioritize customer needs - we have a 48-hour delivery on...
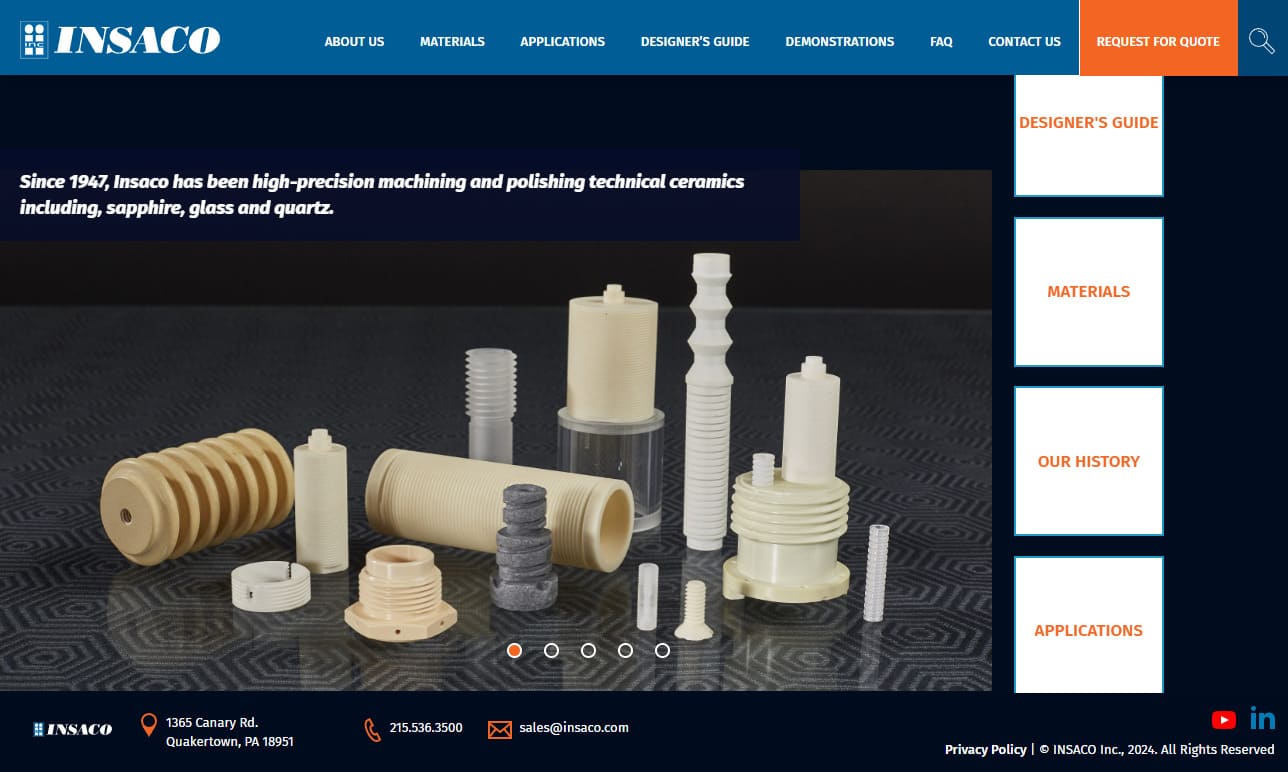
Insaco provides custom grinding and machining services to fabricate precision parts from sapphire, quartz, and most technical ceramics including alumina, zirconia, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, aluminum nitride, and others.
Applied Ceramics is a fabricator of custom-made ceramic parts designed for semiconductor, solar, fuel cell, oil drilling, nuclear, and numerous other industries. Materials include ACI-995 Alumina, Zirconia, and more. Our extensive experience with precision designs supported by our team of specialists ensures that our customers have the ideal solution to meet the needs of their application. To get ...
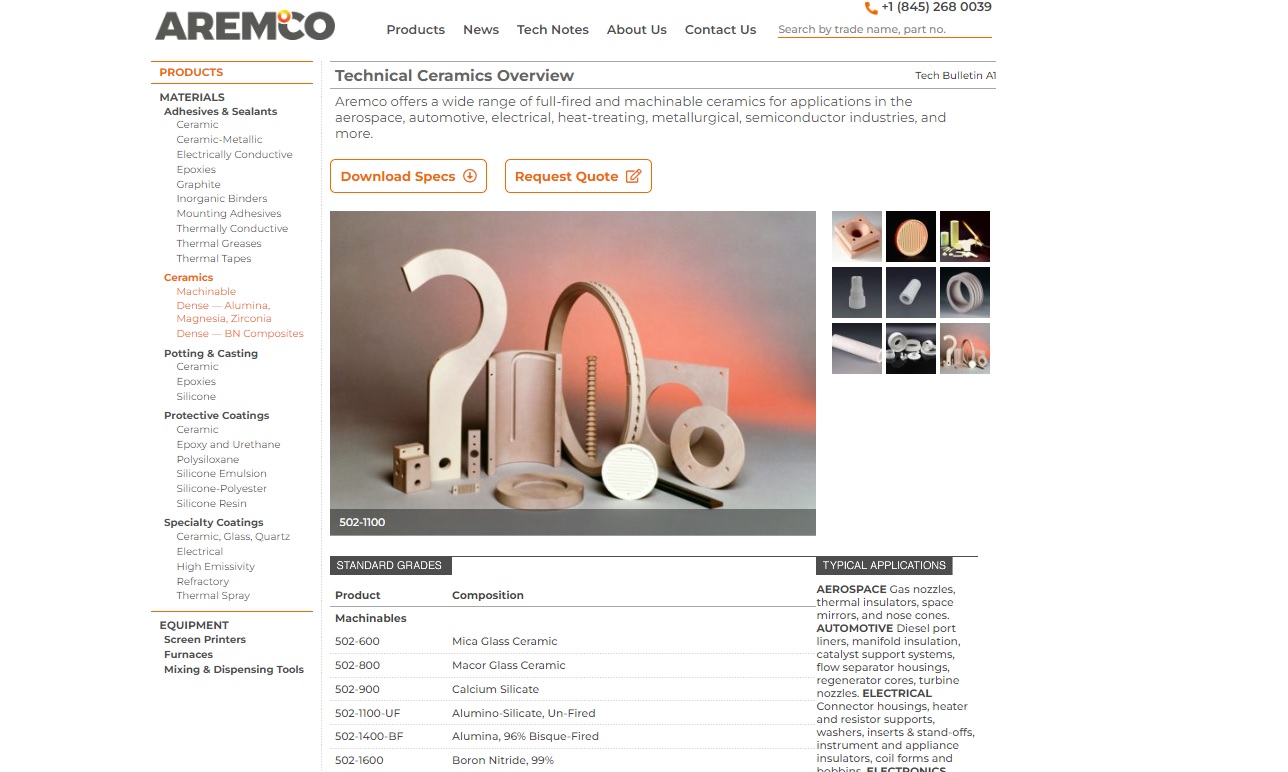
Aremco is a leader in the custom formulation of advanced industrial materials including technical ceramics. Offering many capabilities for a broad range of machinable & dense ceramic materials, Aremco serves aerospace, automotive, electrical, electronics, heat treating, metallurgical, petrochemical & plastics applications with superior finished ceramic parts. 100’s of standard industrial...

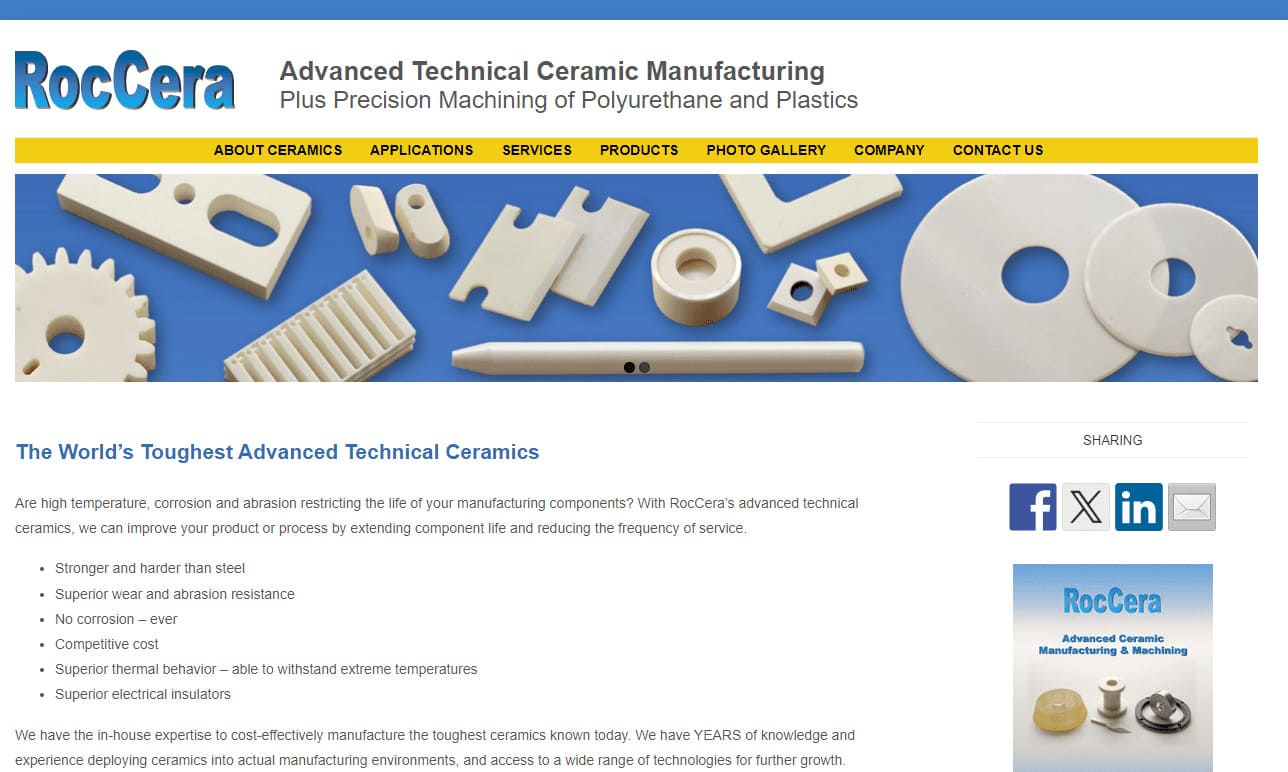
RocCera designs high-performance ceramic components. With a relentless pursuit of excellence and innovation, we have positioned ourselves as a leading provider of custom ceramic solutions catering to a diverse range of industries. Specializing in advanced technical ceramics, RocCera boasts a versatile portfolio that includes the manufacturing of ceramic components for various applications. Our...
As an ISO 9000 and QS 9000 company, CeramTec North America offers ceramic products such as ceramic insulators, ceramic cutting tools, ceramic substrates and ceramic-to-metal joints. We are one of the world's largest ceramic manufacturers that offer custom-engineered high-tech ceramics.
More Industrial Ceramic Manufacturers
What are Industrial Ceramics?
Industrial ceramic materials are made up of non-metallic, inorganic chemicals. Products created from industrial ceramics have a high alumina content . They feature various electrical characteristics, high melting points, and low wear resistance. These materials are very different from ceramics used for art and enjoyment.
All ceramics have certain positive properties, but industrial ceramics must be extremely resistant to a wide range of elements. Traditional brickmakers, glaziers, and potters have traditionally produced ceramic goods using common, naturally occurring minerals like clay and sand. On the other hand, modern advanced ceramics frequently require the talents of a chemist, a physicist, and an engineer to create them under precise laboratory conditions.
How Industrial Ceramics are made
Regardless of the final product, industrial-grade ceramic production starts the same way. First, the appropriate amounts of non-metallic mineral clays are obtained and crushed or ground into a fine powder. Any contaminant in precipitate form can be removed by adding a purification agent or chemical solution.
Next, the residual solution is heated to create an incredibly pure powder. Then, in many instances, tiny amounts of wax are used to bond the grains. Plastics can also be incorporated to improve flexibility and durability.
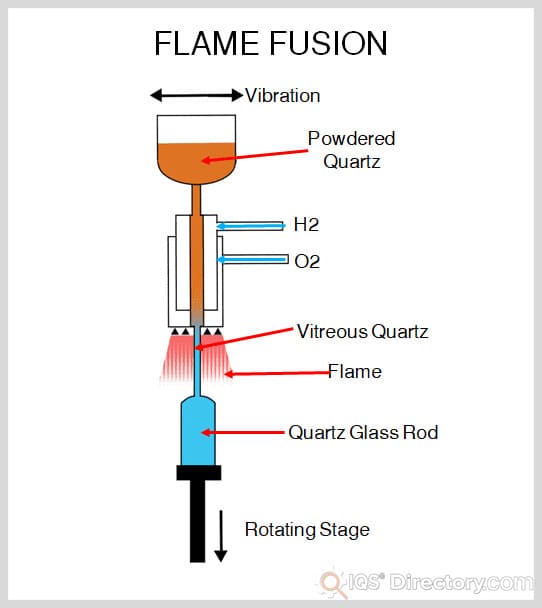
No binding agent is used to fuse ceramics. Instead, the production process itself causes the grains or crystals to connect. Sintering, fire, hot pressing, HIPping, extrusion, fusing, slip or pressure casting, injection molding, and deposition are some techniques that can yield a finished and formed ceramic product.
The materials are then strengthened even further during a densification process that involves heating these items. Industrial environments use a wide variety of ceramic materials. Oxides, carbides, and nitrides are common materials that are frequently combined.
When choosing industrial ceramics, considerations include maximum use temperature, thermal conductivity, rupture modulus, elasticity, electrical resistance, average crystal size, density, and purity.

Types of Industrial Ceramics
- Machinable ceramics can be machined without significant chipping in the green, glass, or final states. They are capable of being shaped in a variety of ways using metalworking tools. Machinable products don't need to be fired or ground after machining, even though the mechanical qualities of machinable ceramics are lower than those of engineering ceramics.
- Porous ceramics act as a thermal barrier thanks to their numerous internal open or closed pores. Without using binders, fused materials join separate grains or crystals together. Instead, these ceramic materials are created using deposition, extrusion, fusing, hot pressing, or fire ceramic elements.
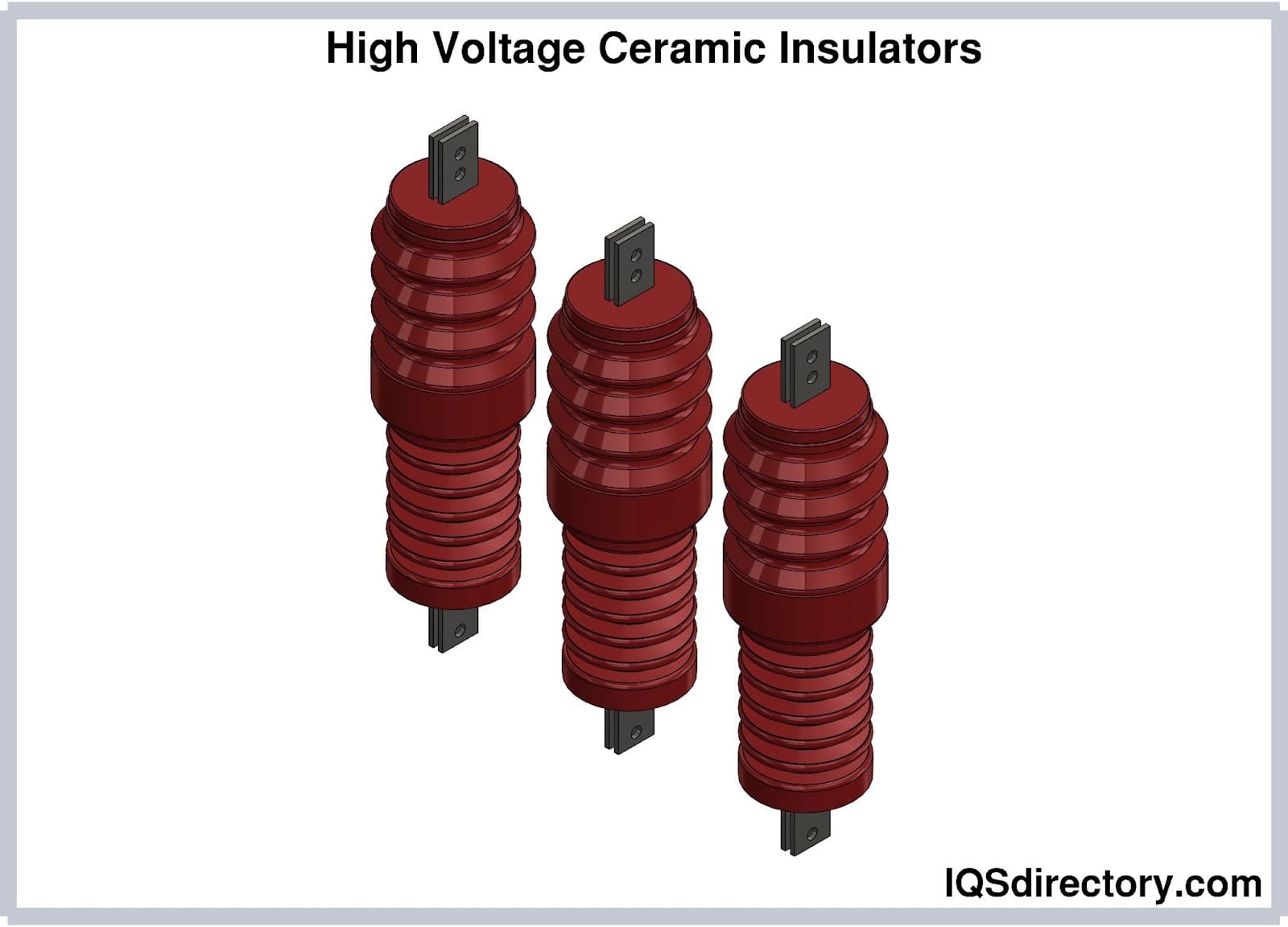
- Refractory ceramics are appropriate for applications needing strong wear resistance, high temperature strength, or electrical or thermal insulation because they have high melting points.
Materials made of structural ceramic are more elastic and have better compressive strengths than metals.
Applications of Industrial Ceramics
- Refractory materials are used in the iron and steel industry as the lining for metal melting furnaces, the ladles that hold, transport, and pour molten metal, and the pipes that remove hot gasses. Refractory materials are also used to make sleeves and other objects required to handle molten metals. Refractories are mostly used in other sectors to construct kilns, furnaces, kiln furniture, and vessels for material processing (e.g., sintering, melting, crystallization, and high-temperature chemical reactions).
- Another important class of ceramic goods for industrial uses is catalysts and catalyst carriers, or substrates and media that support the catalyst. They are largely utilized in petroleum refining and chemical processing to manufacture fuels, polymers, bulk chemicals, and pharmaceuticals that would not otherwise be conceivable and to lessen environmental pollution.
- Ceramics are crucial for the processes of filtration and separation. Products are made up of membranes, macrofiltration media, and filters. The three have different pore sizes: macrofiltration media have pores between 10 and 1,000 microns, while filters have bigger openings. Membranes, which are frequently created with ceramic nanofibers, have very small pore sizes (below 10 microns). Ceramic separation media are preferred for treating fluids with high temperatures or corrosive properties but are less prevalent and more expensive than polymeric media. Additionally, they are less susceptible to fouling and easier to renew using steam and heat treatments. The longer lifespan and decreased downtime offset the greater initial cost.
Choosing the Proper Industrial Ceramics Supplier
To make sure you have the most beneficial outcome when purchasing Industrial Ceramics from an Industrial Ceramics Supplier, it is important to compare at least 6 Manufacturers using our list of Industrial Ceramics suppliers. Each Industrial Ceramics Manufacturer has a business profile page that highlights their areas of experience and capabilities and a contact form to directly communicate with the manufacturer for more information or request a quote. Review each Industrial Ceramics company website using our patented website previewer to get an idea of what each business specializes in, and then use our simple RFQ form to contact multiple companies with the same quote.




 Adhesives
Adhesives Alumina Ceramic
Alumina Ceramic Ceramic
Ceramic Glass
Glass Graphite
Graphite Lubricants
Lubricants Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services