Ceramic electrical insulators are inserted into control boards and boxes as a heat sink but are most frequently employed to create non-conductive bridges between electronic components. They are formed of porous clay that is either red, brown, or white, and they have high dielectric strength and steady and minimal electrical loss. In addition, they are simple to maintain and immune to stains and other residue types. Because of their incredibly high electrical current resistance, ceramics have been utilized as electric insulators for a long time. Read More…
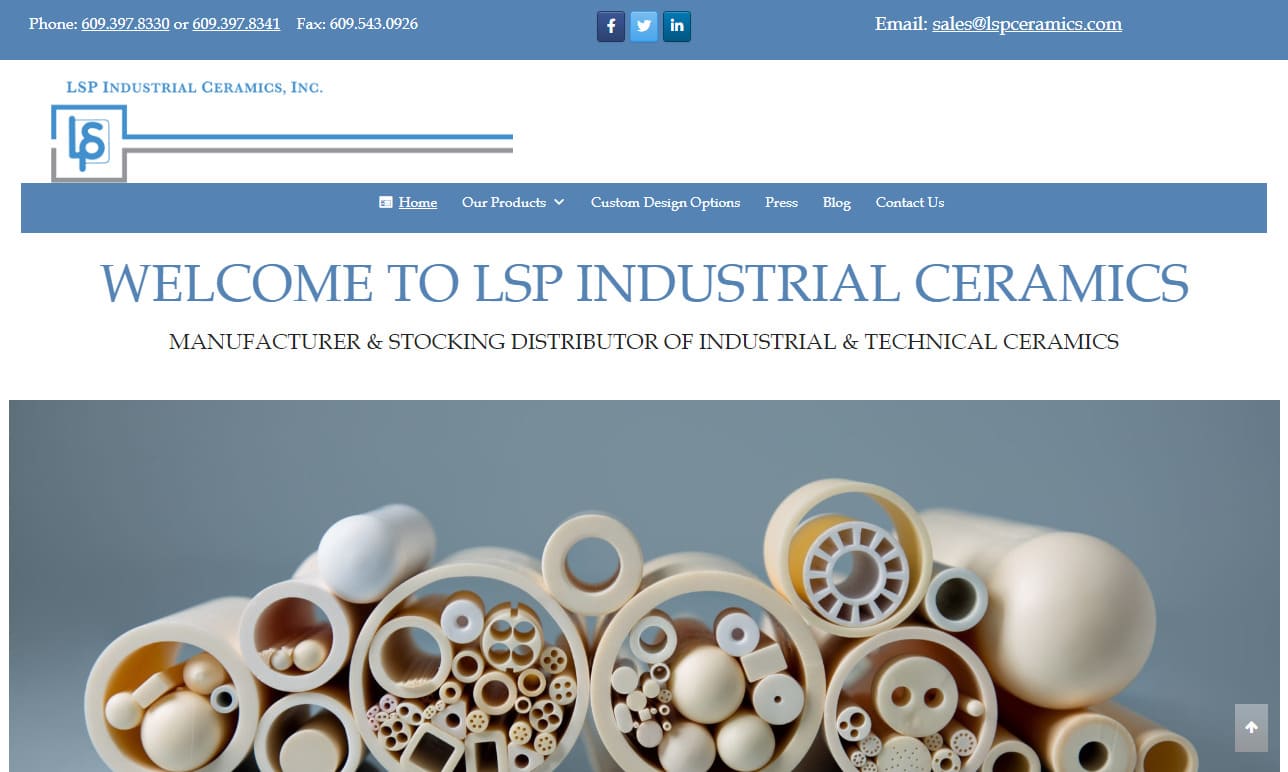
As a manufacturer and stocking distributor of industrial and technical ceramics, LSP carries the most diversified inventory of ceramic tubes, spacers, bushings, etc. in the industry.
C-Mac International manufactures custom advanced technical ceramic solutions. Our specialties are Zirconia (MgO stabilized and Yttria stabilized), Alumina (90%, 96%, and 99.5% purity), and Tungsten Carbide (Cobalt and Nickel Binder). We also work with steatite, cordierite, silicon nitride, ceramic crucibles, and crushable ceramics. We prioritize customer needs - we have a 48-hour delivery on...
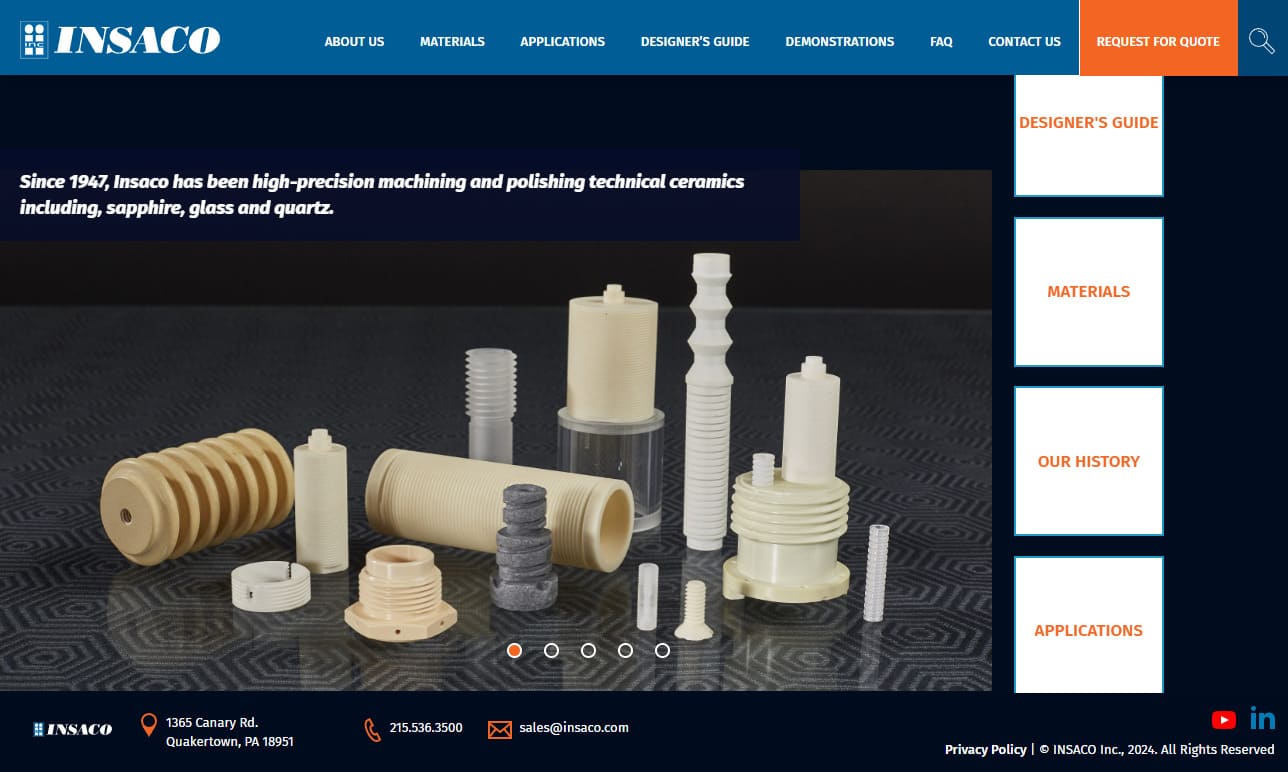
Insaco provides custom grinding and machining services to fabricate precision parts from sapphire, quartz, and most technical ceramics including alumina, zirconia, silicon carbide, silicon nitride, aluminum nitride, and others.
Applied Ceramics is a fabricator of custom-made ceramic parts designed for semiconductor, solar, fuel cell, oil drilling, nuclear, and numerous other industries. Materials include ACI-995 Alumina, Zirconia, and more. Our extensive experience with precision designs supported by our team of specialists ensures that our customers have the ideal solution to meet the needs of their application. To get ...
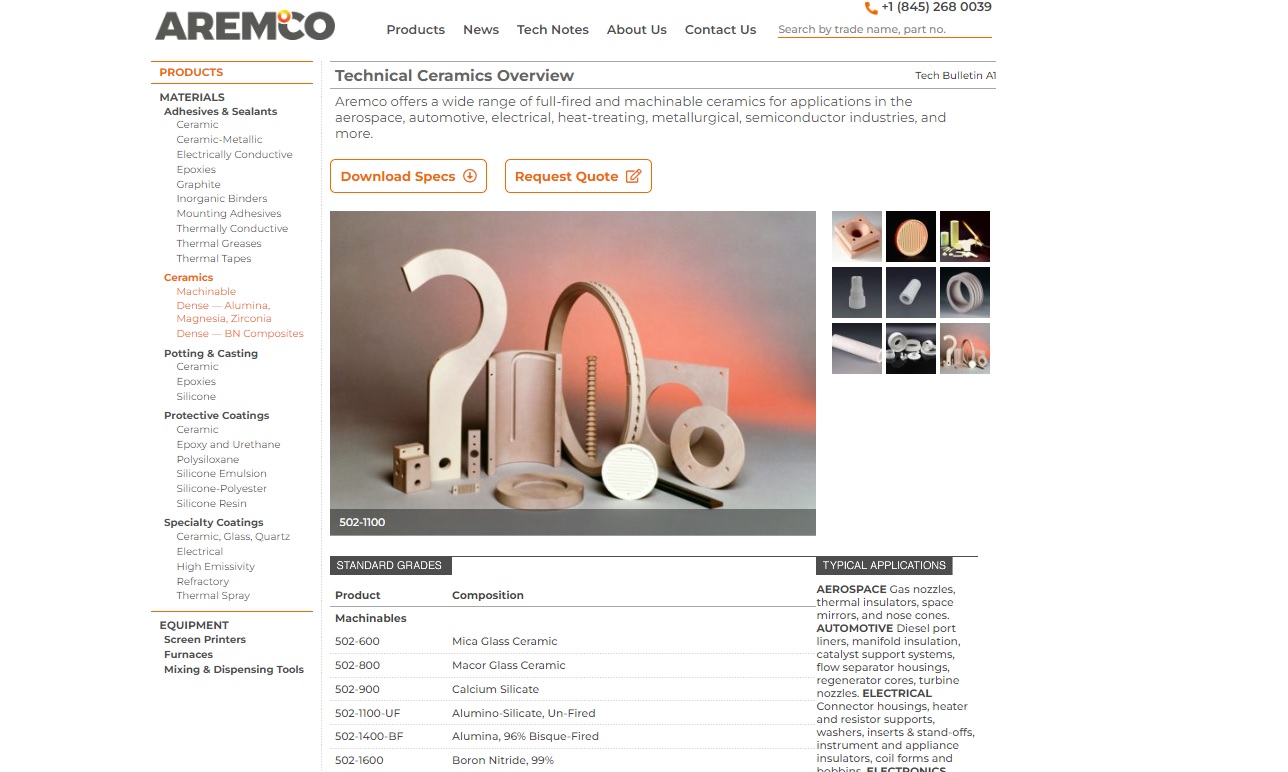
Aremco is a leader in the custom formulation of advanced industrial materials including technical ceramics. Offering many capabilities for a broad range of machinable & dense ceramic materials, Aremco serves aerospace, automotive, electrical, electronics, heat treating, metallurgical, petrochemical & plastics applications with superior finished ceramic parts. 100’s of standard industrial...

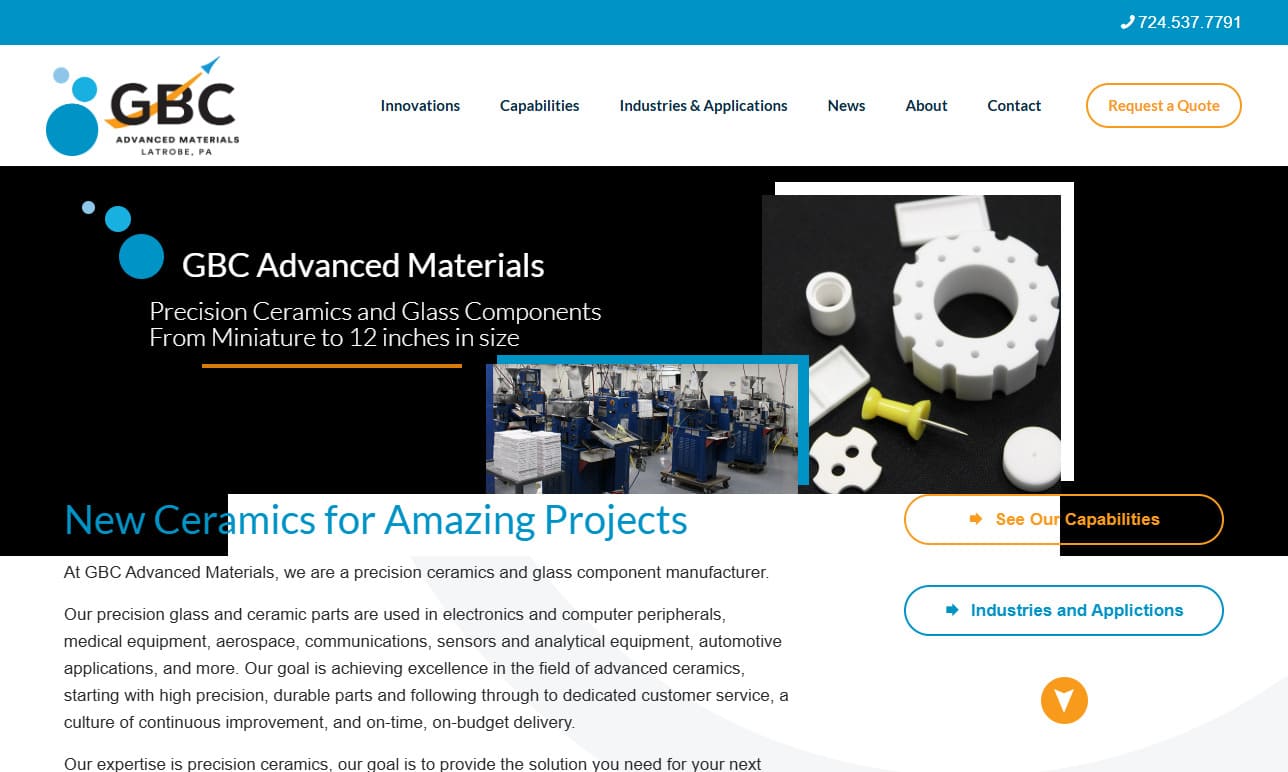
GBC Advanced Materials is a leading provider of advanced ceramic solutions, specializing in a wide range of iso-pressing techniques, green machining, sintering, extrusion, and CNC grinding. With a focus on innovation, precision, and quality, we offer comprehensive capabilities to meet the diverse needs of industries worldwide.

At Superior Technical Ceramics Corp., we take pride in engineering and manufacturing advanced ceramic components that push the boundaries of performance and reliability. With decades of specialized experience, we have built our reputation on precision, innovation, and the ability to meet the most demanding requirements across industries.

More Ceramic Insulator Manufacturers

How Ceramic Insulators are Used
Ceramic insulators play an essential role in a wide range of electrical and electronic applications, serving as the backbone for electrical insulation across industries. Their use extends from high-voltage power distribution centers to the intricate wiring found in mobile phones and consumer electronics. Thanks to their exceptional non-conductive properties, high dielectric strength, and remarkable mechanical robustness, ceramic insulators are considered one of the most reliable insulating materials available today. Their widespread adoption is driven by their ability to shield against electromagnetic interference (EMI), mitigate fire risks, prevent power surges, and reduce the likelihood of short circuits or electrical faults.
Whether used in power transmission lines, coaxial cables, printed circuit boards (PCBs), or industrial machinery, ceramic insulators provide a protective barrier that maintains system integrity and ensures user safety. Their superior heat retention and resistance to thermal shock make them the preferred choice in environments exposed to extreme temperatures, such as electrical furnaces and kilns. Ceramics can also be easily manufactured into a variety of complex shapes and sizes, allowing engineers and designers to tailor insulator solutions for specific applications. This versatility further cements their role as a foundational component in modern electrical and electronic systems.
Are you researching the best insulating materials for your next power distribution project? Or perhaps you’re comparing ceramic insulators with alternatives like glass, polymer, or composite insulators? Understanding the unique advantages of ceramics can help you make an informed decision. Keep reading to explore use cases, benefits, and selection criteria for ceramic insulators.
Uses of Ceramic Insulators
Poles
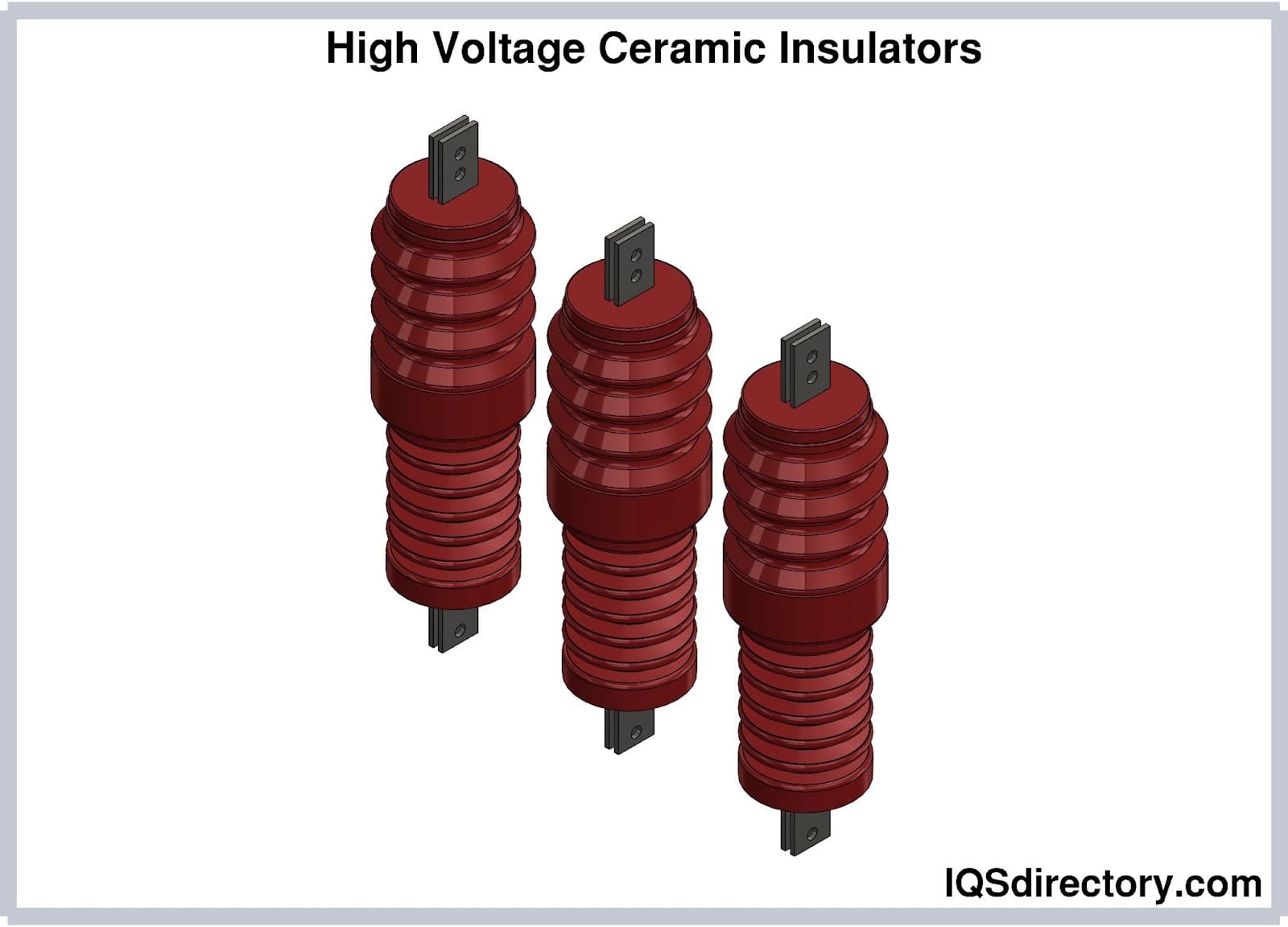
One of the most common and visually recognizable applications of ceramic insulators is on utility poles and transmission towers. The classic spool or “pin-type” ceramic insulator is typically attached to a bracket, secured by a central rod running through the insulator’s axis. This configuration allows for secure mounting to surfaces such as walls, poles, or ceilings, ensuring stability even when the direction or angle of the connected power line changes. These ceramic pole insulators are engineered to withstand environmental stresses—such as wind, rain, and pollution—while maintaining reliable electrical insulation and mechanical support for overhead power lines, telecommunication cables, and railway electrification systems.
Considering upgrading your infrastructure with high-performance insulators for outdoor environments? Learn more about the advantages of ceramic pole insulators and how they compare to modern polymer alternatives in terms of durability and cost-effectiveness.

Safety
Safety is at the core of every electrical system, and ceramic insulators are specifically designed to control current flow and prevent dangerous leakages to the ground. In the event of a wire being severed or a pole collapsing, these insulators ensure that live conductors remain isolated from the earth, mitigating the risk of electrical shock and fire hazards. The robust placement and design of safety ceramic insulators maintain the integrity of suspended wires, preventing unintended contact with grounded surfaces. Depending on application requirements, these insulators are manufactured in various shapes and connection types to adapt to diverse installation scenarios, from residential wiring to industrial power grids.
Curious about how ceramic insulators enhance safety in high-risk environments? Discover best practices for implementing safety insulators in both indoor and outdoor settings to maximize protection for personnel and equipment.
Heat Applications
In environments where intense heat is generated—such as furnaces, industrial ovens, and electric heaters—ceramic insulators are the material of choice for supporting and separating heating elements. Their unique combination of thermal stability, chemical inertness, and mechanical strength allows them to maintain performance even under continuous thermal cycling and high-pressure conditions. Ceramic materials retain their insulating properties at temperatures where plastics and other materials would fail, making them indispensable in applications like kilns, heat treatment chambers, and high-temperature laboratory equipment.
Need reliable insulation for industrial heating systems? Explore how ceramic insulators can extend equipment lifespan, reduce maintenance costs, and improve energy efficiency in demanding thermal environments.
Mechanical Stress
Ceramic insulators are also engineered to provide superior mechanical strength, particularly in applications where wires or cables are subject to significant tension or pulling forces. These tension-type insulators are commonly found in overhead power transmission systems, radio antennas, and communication towers. By maintaining the separation and correct positioning of conductors, ceramic insulators with mechanical tension capabilities help prevent sagging, electrical arcing, and inadvertent contact between lines. Their durability ensures long-term performance, even in harsh weather conditions or under heavy mechanical loads.
If you’re facing challenges with maintaining cable tension or preventing line sag in your electrical installations, consider the benefits of using high-strength ceramic tension insulators for optimal system reliability.
Types of Ceramic Insulators
Ceramic Standoff Insulators
Ceramic standoff insulators are vital for isolating electrical components in assemblies where current control and creepage distance are critical. By directing electrical current along intended paths and blocking unintended conduction between adjacent parts, standoff insulators are widely used in transformer current regulators, switchgear, and power distribution panels. Their design minimizes energy loss and power dissipation, contributing to higher system efficiency and safety.
Engineers often select ceramic standoff insulators for their ability to withstand high temperatures generated by heavy-duty resistors and power electronics. Available in a variety of cylindrical, square, and custom shapes, these insulators provide secure mounting for fuses, busbars, and high-voltage cables. Their adaptability makes them an excellent solution for complex electrical layouts where space and performance are at a premium.
Looking for high-voltage standoff insulators for your control panel or transformer project? Compare size, voltage rating, and mounting options to find the best ceramic standoff insulator for your needs.
Ceramic Suspension Insulators
Suspension-type ceramic insulators are designed to support long spans of overhead electrical lines, especially in high-voltage transmission systems. These insulators are typically assembled as “strings” of disk-shaped units, each joined by rugged metal fittings. The modular configuration allows for adjustment of the total string length and insulation level, making them suitable for both standard and extra-high-voltage (EHV) applications. Suspension insulators excel at minimizing flashover risks, accommodating mechanical stress, and providing robust performance in polluted or coastal environments.
Are you designing a high-voltage transmission network? Learn how ceramic suspension insulators can improve reliability and reduce maintenance costs in challenging outdoor conditions.
Hollow Ceramic Insulators
Hollow ceramic insulators are indispensable in applications demanding both electrical isolation and the ability to accommodate moving parts or conductors passing through insulated barriers. Commonly used as bushings for power and instrument transformers, circuit breakers, surge arresters, and cable terminations, these insulators are manufactured in a wide range of sizes and shapes—such as cylindrical, conical, or spherical bodies. Their high mechanical resistance and superior dielectric properties make them ideal for heavy-duty industrial and utility-scale installations.
Do you need custom hollow insulators for specialized switchgear or transformer projects? Explore how different body shapes and material compositions can be optimized for your specific voltage, mechanical, and environmental requirements.
Ceramic Insulator Benefits
High Dielectric Strength
One of the defining advantages of ceramic insulators is their extremely high dielectric strength, which allows them to withstand strong electric fields without breaking down. This property makes them suitable for a vast array of electrical wiring, high-voltage circuits, and electronic assemblies. Whether deployed in utility substations or compact consumer devices, ceramic insulators consistently deliver outstanding performance, even under adverse conditions.
Comparing different insulator materials? Discover why engineers choose ceramics for high-voltage and high-frequency applications where dielectric strength is paramount.
Corrosion and Weather Resistance
Unlike metal-based insulators, ceramic insulators are entirely resistant to rust, corrosion, and chemical attack. This makes them ideal for use in outdoor environments, including fence posts, power line crossarms, and exterior electrical networks exposed to humidity, salt spray, pollutants, and UV radiation. Their stable performance over decades reduces the need for frequent replacements and lowers the total cost of ownership.
Want to minimize maintenance on your outdoor electrical installations? Examine how ceramic insulators outperform polymers and composites in terms of weatherability and long-term stability.
Exceptional Hardness and Mechanical Durability
Despite being derived from fine powders and natural minerals, ceramic insulators exhibit remarkable hardness—often surpassing the strength of stainless steel by a factor of four. This inherent toughness ensures that ceramic components can endure repeated mechanical stresses, impacts, and vibrations without cracking or deforming. Their robust structure is crucial for ensuring the integrity of power transmission lines, especially in regions prone to storms, seismic activity, or high winds.
Are you specifying insulators for a critical infrastructure project? Learn how ceramic material properties contribute to system resilience and reliability in demanding environments.
Wear and Abrasion Resistance
The exceptional wear resistance of ceramic insulators complements their hardness, ensuring that their insulating surfaces remain intact and effective even after years of exposure to dust, grit, and abrasive contaminants. This is particularly important in dusty industrial sites, manufacturing plants, and transportation networks, where mechanical wear can accelerate the degradation of lesser materials.
Looking for insulators that can withstand abrasive environments? Evaluate the long-term benefits of ceramics for industrial and transportation applications.
Stable Technical and Mechanical Properties
For any component designed to protect electrical wiring or equipment, maintaining mechanical integrity and consistent performance over time is critical. Ceramic insulators retain their technical characteristics—such as shape, size, and dielectric properties—even after prolonged exposure to thermal cycling, chemical exposure, and physical stress. Their stability translates to fewer failures, reduced downtime, and improved system safety over the product lifecycle.
Worried about the reliability of your electrical insulation? Discover how the inherent stability of ceramic insulators supports safe and consistent operation in mission-critical systems.

Industry Applications and Market Trends for Ceramic Insulators
Ceramic insulators continue to be the preferred choice for a broad spectrum of industries due to their unique combination of electrical, thermal, and mechanical properties. Key sectors utilizing ceramic insulators include:
- Power generation and transmission – High-voltage substations, overhead lines, transformers, and switchgear
- Electronics manufacturing – Printed circuit boards, semiconductor devices, and consumer electronics
- Telecommunication infrastructure – Antenna insulators, cable supports, and radio towers
- Railways and transportation – Electrified rail lines, signaling equipment, and traction systems
- Industrial heating and processing – Ovens, kilns, furnaces, and laboratory equipment
- Renewable energy – Wind turbine generators, solar power installations, and energy storage systems
Recent advances in ceramic material science—such as the development of alumina, steatite, and zirconia-based insulators—have further expanded the performance envelope, enabling higher voltage ratings, improved mechanical resilience, and enhanced resistance to pollution and environmental stress. As the global demand for reliable power infrastructure and advanced electronics grows, so does the need for high-quality ceramic insulators tailored to new and emerging applications.
Interested in market trends and future applications for ceramic insulators? Explore how the electrification of transportation, growth in renewable energy, and Industry 4.0 are driving innovation in insulator design and manufacturing.
Buyer’s Guide: Choosing the Right Ceramic Insulator
Selecting the optimal ceramic insulator for your application requires careful consideration of several factors. Key decision points include:
- Voltage and electrical requirements – Ensure the insulator’s dielectric strength matches or exceeds system voltages.
- Mechanical load and installation environment – Assess the insulator’s ability to withstand physical stresses, mount securely, and resist environmental challenges.
- Thermal performance – Confirm the material’s stability at operating temperatures, especially in high-heat applications.
- Shape, size, and mounting configuration – Select dimensions and connection types compatible with your system architecture.
- Industry certifications and standards – Look for compliance with IEC, ANSI, or other relevant standards to ensure safety and quality.
- Supplier reliability and customization options – Partner with experienced manufacturers who offer technical support, custom designs, and timely delivery.
Still not sure which ceramic insulator is best for your project? Contact our team for expert guidance or request a quote from leading manufacturers.
Comparing Ceramic Insulators with Alternative Materials
While ceramic insulators are renowned for their performance, engineers often weigh them against other materials such as glass, polymers, and composite insulators. Key points of comparison include:
- Electrical and mechanical reliability – Ceramics outperform polymers in high-temperature and high-voltage environments, while glass insulators can be susceptible to breakage from impact.
- Weather and pollution resistance – Ceramic and glass resist weathering and pollution well, but modern hydrophobic polymer coatings can offer self-cleaning properties.
- Weight and handling – Polymer and composite insulators are lighter and easier to install, but may not match the longevity and mechanical strength of ceramics.
- Cost of ownership – While initial costs may be lower for polymer insulators, ceramics typically offer a lower total cost over their service life due to reduced maintenance and replacement needs.
Evaluating insulator material options for your project? Review case studies and performance comparisons to make the most informed decision for your electrical system’s safety and reliability.
Choosing the Proper Ceramic Insulators Supplier
To achieve the best results when purchasing ceramic insulators, it’s crucial to work with a reputable ceramic insulator supplier. We recommend comparing at least six manufacturers using our comprehensive list of ceramic insulator suppliers. Each supplier profile highlights core competencies, manufacturing capabilities, and unique areas of expertise. You can use integrated contact forms to request quotes, technical data, and lead time information directly from multiple suppliers at once.
Before making a purchasing decision, review each ceramic insulator company website using our proprietary website previewer to assess their product range, certifications, and customer support. Our streamlined RFQ form lets you efficiently contact multiple ceramic insulator companies with a single submission, simplifying your procurement workflow.
Ready to find the right partner? Browse our directory of ceramic insulator suppliers or reach out for personalized assistance from our team of industry experts.
Frequently Asked Questions about Ceramic Insulators
- What are the main advantages of ceramic insulators compared to glass or polymer types?
Ceramic insulators offer superior mechanical strength, high dielectric strength, excellent thermal stability, and outstanding resistance to corrosion and environmental degradation. These factors make ceramics the preferred choice for demanding high-voltage and outdoor applications. - How do I select the right ceramic insulator for my application?
Consider factors such as voltage rating, mechanical load, installation environment, thermal requirements, and compliance with industry standards. Consulting with experienced suppliers can help ensure an optimal match for your project’s needs. - Can ceramic insulators be customized for unique applications?
Yes, many manufacturers offer custom design and manufacturing services for ceramic insulators, including specific shapes, sizes, mounting hardware, and material formulations to meet unique performance requirements. - What is the typical lifespan of a ceramic insulator?
With proper installation and minimal maintenance, ceramic insulators can last several decades—even in challenging outdoor or industrial environments. - Where can I source high-quality ceramic insulators for my next project?
Use our supplier directory to connect with leading manufacturers, compare offerings, and request technical information or quotes tailored to your needs.
Conclusion
Ceramic insulators remain an indispensable component in modern electrical and electronic systems, prized for their unparalleled insulating properties, durability, and ability to perform under the most demanding conditions. Whether you’re designing high-voltage power lines, building advanced electronic devices, or upgrading industrial heating systems, choosing the right ceramic insulator is essential for safety, performance, and long-term reliability.
Ready to take the next step? Explore our full range of ceramic insulators, request a quote, or contact our team for expert advice on your specific application.




 Adhesives
Adhesives Alumina Ceramic
Alumina Ceramic Ceramic
Ceramic Glass
Glass Graphite
Graphite Lubricants
Lubricants Castings & Forgings
Castings & Forgings Bulk Material Handling
Bulk Material Handling Electrical & Electronic Components
Electrical & Electronic Components Flow Instrumentation
Flow Instrumentation Hardware
Hardware Material Handling Equipment
Material Handling Equipment Metal Cutting Services
Metal Cutting Services Metal Forming Services
Metal Forming Services Metal Suppliers
Metal Suppliers Motion Control Products
Motion Control Products Plant & Facility Equipment
Plant & Facility Equipment Plant & Facility Supplies
Plant & Facility Supplies Plastic Molding Processes
Plastic Molding Processes Pumps & Valves
Pumps & Valves Recycling Equipment
Recycling Equipment Rubber Products & Services
Rubber Products & Services